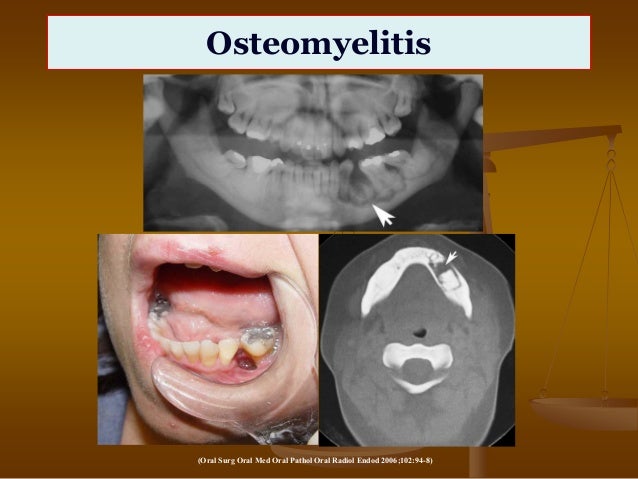
Osteomyelitis is the inflammation of bone secondary to hematogenous or traumatic spread of bacteria or fungal organisms. Signs of acute osteomyelitis can include fever, lethargy, pain, and soft tissue swelling.
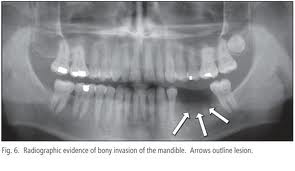
Osteomyelitis (OM) is an inflammatory condition of bone that involves the medullary cavity and the adjacent cortex. It occurs more frequently in mandible than in the maxilla and is often associated with suppuration and pain.1 The osseous spaces are usually filled with exudates that can lead to pus
Osteomyelitis is a relatively rare complication of dental extractions that can mimic multiple benign and malignant processes, making it difficult to recognize in otherwise healthy patients.



Newburyport Oral Surgery is a private practice limited to oral and maxillofacial surgery. The hallmark of this practice has been our unique ability to deliver the high standards of practice found at hospital-based facilities while maintaining the tradition of a small, family-oriented, private office.
### Diabetic Osteomyelitis ★★ Treating Diabetic Patient With Prednisone The 3 Step Trick that Reverses Diabetes Permanently in As Little as 11 Days.[ DIABETIC OSTEOMYELITIS ] The REAL cause of Diabetes ( Recommended )

INTRODUCTION. Vertebral osteomyelitis most often occurs as a result of hematogenous seeding of one or more vertebral bodies from a distant focus [].Infection may also involve the adjacent intervertebral disc space, which has no direct blood supply in adults.
A bone infection, also called osteomyelitis, can result when bacteria or fungi invade a bone. In ren, bone infections most commonly occur in the long bones of the arms and legs. In adults, they usually appear in the hips, spine, and feet. Bone infections can happen suddenly or develop over a
INTRODUCTION. Osteomyelitis is one of the oldest recorded diseases, with descriptions dating back to the time of Hippocrates (460 to 370 BC) [].Terms such as “abscessus in medulla,” “necrosis,” and “a boil of the bone marrow” were used to describe the infection until Nélaton introduced the term “osteomyelitis” in 1844.

Osteomyelitis — Comprehensive overview covers symptoms, causes, treatment of chronic and acute bone infections.

(OBQ11.29) A 9-year-old man is being treated for acute hematogenous osteomyelitis of the distal tibia with appropriate IV antibiotic therapy. After three days of treatment, he fails to show any clinical improvement.