Uniform circular motion. 9-29-99 Sections 5.1 – 5.2 Uniform circular motion. When an object is experiencing uniform circular motion, it is traveling in a circular …

HTML5 app: Uniform circular motion. Circular motion plays an important role in nature and technology. So, the planets move on (approximately) circular orbits around the sun.
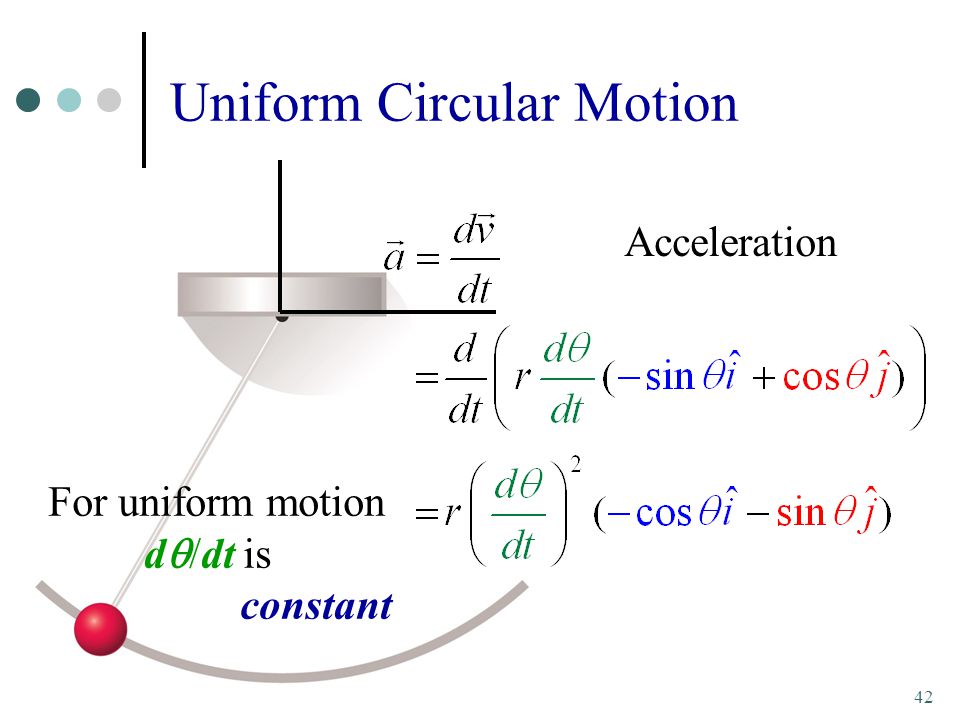
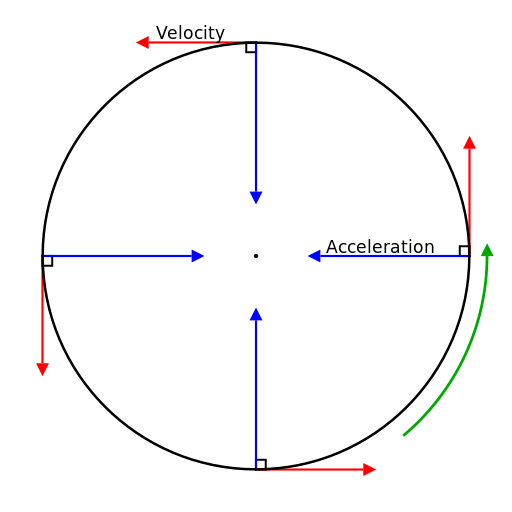
In addition to any tangential acceleration, there is always the centripetal acceleration:. The angular displancment is defined by: For a circular path it …

Using the Interactive The Uniform Circular Motion Interactive is shown in the iFrame below. There is a small hot spot in the top-left corner.



Circular motion with animations and video film clips. Why cars take off on hills. Physclips provides multimedia education in introductory …
Uniform Circular Motion The Uniform Circular Motion Interactive provides the learner with an interactive, variable-rich environment for exploring principles and relationships related to moving in a circle at a constant speed.
In physics, circular motion is a movement of an object along the circumference of a circle or rotation along a circular path. It can be uniform, with constant angular rate of rotation and constant speed, or non-uniform with a changing rate of rotation.

Investigate how torque causes an object to rotate. Discover the relationships between angular acceleration, moment of inertia, angular momentum and torque.
Regents Physics – Uniform Circular Motion Centripetal Acceleration. The motion of an object in a circular path at constant speed is known as uniform circular motion (UCM). An object in UCM is constantly changing direction, and since velocity is a vector and has direction, you could say that an object undergoing UCM has a constantly …
Instantaneous acceleration, meanwhile, is the limit of the average acceleration over an infinitesimal interval of time. In the terms of calculus, instantaneous acceleration is the derivative of the velocity vector with respect to time:

